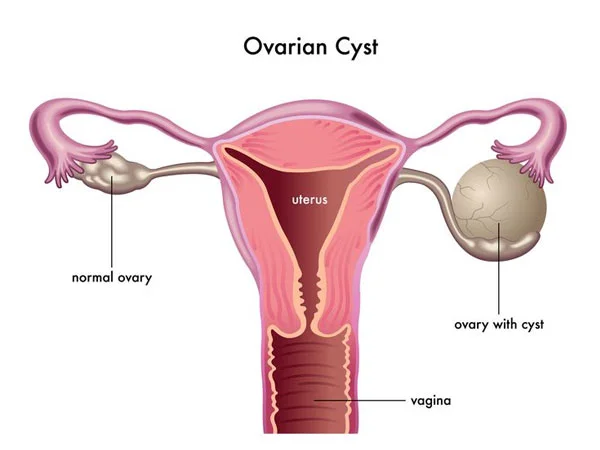
Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms on or within the ovary, which is a part of the female reproductive system. Ovarian cysts are common and can occur at various stages of a woman’s life, from puberty to menopause.
What causes Ovarian Cyst?
There are several potential causes of ovarian cysts, including:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during the menstrual cycle, can cause the formation of ovarian cysts. For example, follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts are two types of cysts that can form due to hormonal imbalances during the normal menstrual cycle.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause the ovaries to enlarge and develop multiple cysts. It is one of the most common causes of ovarian cysts, and it can disrupt the normal hormonal balance in the body.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, including on the ovaries. This can cause the formation of ovarian cysts known as endometriomas.
- Functional Cysts: Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cysts and typically form during the normal menstrual cycle. They are usually harmless and resolve on their own without treatment. Examples of functional cysts include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts.
- Cystadenomas: Cystadenomas are ovarian cysts that form from the outer surface of the ovary and can be filled with either fluid or mucus. They are usually benign (non-cancerous) but can become large and cause discomfort.
- Dermoid Cysts: Dermoid cysts, also known as mature cystic teratomas, are ovarian cysts that can contain tissues such as hair, skin, teeth, and even bone. They are typically benign but can cause pain or discomfort.
- Ovarian Cancers: In rare cases, ovarian cysts can be associated with ovarian cancers. These cysts are usually solid and may require medical evaluation and treatment.
Ovarian cysts can be classified into different types, including functional cysts and pathological cysts.
Functional cysts : Functional cysts are benign (non-cancerous) ovarian cysts that develop as a result of the normal menstrual cycle or hormonal changes in the ovaries. They are the most common type of ovarian cysts and typically do not cause any symptoms or require treatment, as they often resolve on their own without causing any harm. Functional cysts are usually small and temporary, and they can occur in women of reproductive age, from adolescence to menopause.
Pathological cysts : on the other hand, may require medical attention as they can be associated with underlying conditions or diseases.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of ovarian cysts can vary depending on their size, location, and type. Some common symptoms may include
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Bloating
- changes in menstrual cycle
- Pain during intercourse, and frequent urination.
- In some cases, ovarian cysts may cause complications such as ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary), rupture, or bleeding, which may require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts usually involves a pelvic examination, imaging tests such as ultrasound, and sometimes blood tests.
Treatment:
Treatment options for ovarian cysts depend on various factors such as the type, size, and symptoms of the cyst, as well as the woman’s age and overall health. Small, asymptomatic cysts may not require treatment and may be monitored through regular follow-up. However, larger cysts or those causing significant symptoms may require medical intervention, which may include medication to manage pain or hormonal medications to regulate the menstrual cycle. In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove the cyst, especially if it is large, persistent, or suspected to be cancerous.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management of ovarian cysts. They can provide personalized medical advice based on an individual’s specific condition and circumstances.
