Ovarian Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are several types of ovarian cysts, each with its unique characteristics. The two main categories are functional cysts and complex cysts.
- Functional Cysts:
- Follicular Cysts: These are the most common type and form when an ovarian follicle, which is a small sac containing an immature egg, doesn’t release the egg and continues to grow.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: These develop when the follicle releases the egg but doesn’t shrink as it should. They may occasionally result in bleeding and pain.
- Complex Cysts:
- Dermoid Cysts: These cysts are formed from cells that produce eggs and may contain tissues like hair or teeth.
- Endometriomas: These cysts are associated with endometriosis, a condition where the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts develop from the ovarian tissue and can be filled with a watery or mucous-like substance.
Ovarian Cyst Causes
The exact cause of ovarian cysts can vary, depending on the type of cyst. Common causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to the development of functional cysts, like follicular or corpus luteum cysts.
- Endometriosis: This condition can lead to the formation of endometriomas or other types of cysts.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS can result in the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries.
- Pregnancy: Corpus luteum cysts can occur during early pregnancy.
- Ovulation Issues: Irregular or infrequent ovulation can contribute to the development of ovarian cysts.
Ovarian Cyst Symptoms
Many women with ovarian cysts do not experience any symptoms, and the cysts often resolve on their own. When symptoms do appear, though, they can be minor or severe. Common ovarian cyst symptoms include:
- Ovary Pain: Dull aching or sharp pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, which may come and go.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Changes in the menstrual cycle, including heavy or painful periods.
- Painful Intercourse: Unease or discomfort experienced during sex.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or bloating in the lower abdomen.
- Frequent Urination: The need to urinate more often than usual.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Constipation or difficulty passing stools.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may occur if a cyst becomes twisted or ruptures.
Burst Ovarian Cyst Symptoms
- Sudden, intense abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever
- Weakness or dizziness
- Rapid breathing
- Fainting
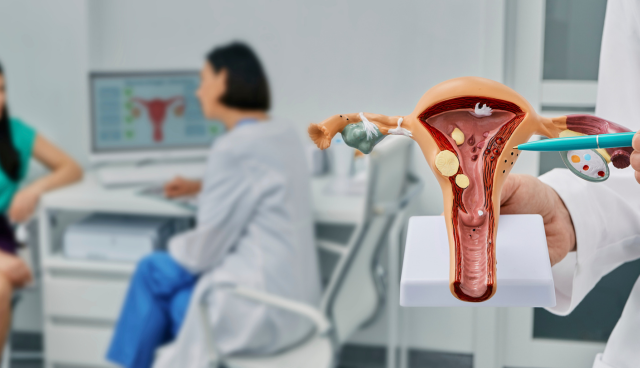
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
If you suspect you have ovarian cysts or are experiencing any symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Usually, they’ll carry out a comprehensive assessment, which could include:
- Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will perform a pelvic examination to feel for any abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan can help visualize the ovaries and the cysts, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Blood Tests: CA-125 blood tests may be ordered to check for a protein that can be elevated in some cases of ovarian cancer. However, this test is not definitive for diagnosing cysts.
Ovarian Cyst Treatment
The treatment of ovarian cysts depends on various factors, including the type of cyst, its size, and whether you are experiencing symptoms. Here are some common treatment options:
- Watchful Waiting: If the cyst is small and not causing any symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend monitoring it over time to see if it goes away on its own. This approach is often taken for functional cysts.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage ovarian cyst pain and discomfort.
- Hormonal Birth Control: Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, can regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new cysts.
- Surgical Removal: If the cyst is large, causing severe symptoms, or appears suspicious, your healthcare provider may recommend surgery. There are two main surgical options:
- Ovarian Cystectomy: This procedure involves removing only the cyst, leaving the ovaries intact.
- Oophorectomy: In some cases, the entire ovary may need to be removed, especially if the cyst is large, complex, or cancerous.
